Cloud computing
Cloud computing has created a radical shift in expanding the reach of application usage and has emerged as a de-facto method to provide low-cost and highly scalable computing services to its users. Existing cloud infrastructure is a composition of large-scale networks of datacenters spread across the globe. These datacenters are carefully installed in isolated locations and are heavily managed by cloud providers to ensure reliable performance to its users. In recent years, novel applications, such as Internet of Things, augmented reality, autonomous vehicles etc. have proliferated the Internet.
Majority of such applications are known to be time-critical and enforce strict computational delay requirements for acceptable performance. Traditional cloud offloading techniques are inefficient for handling such applications due to the incorporation of additional network delay encountered while uploading pre-requisite data to distant datacenters. Furthermore, as computations involving such applications often rely on sensor data from multiple sources, simultaneous data upload to the cloud also results in significant congestion in the network.
Please see video clip "Cloud Computing Services Models - IaaS PaaS SaaS Explained": https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=36zducUX16w&pbjreload=101
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of hosted services that are made available over the Internet. Cloud computing relies on sharing computing resources to handle applications. Computer resources are consumed as a utility such as electricity rather than having to build and maintain in-house computing infrastructures. The NIST defines cloud computing as "a model to enable ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computer resources such as networks, servers, storage, applications and services that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction". According to the NIST, the cloud model is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models and four deployment models as described in Picture 1.
Cloud computing is a set of forms that contain certain elements that allows for on-demand, network access, scalability, and shared resources. It's a platform for managing, storing, and processing data online through the internet.
Some of the cloud computing features include the following:
- On-Demand Services – Available when you need it
- Network Access – When using the internet as your medium
- Shared Resources – All resources are gathered together and used by multiple customers
- Scalability - The ability of a computer system to adapt to increasing demands
The Three Delivery Models
Cloud computing provides different services based on three delivery configurations. When they are arranged in a pyramid structure, they are in the order of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
The Three Services:
SaaS - Software as a Service
This service provides on-demand pay per use of the application software for users and is independent of a platform. You do not have to install software on your computer, unlike a license paid program. Cloud runs a single occurrence of the software, making it available for multiple end-users allowing the service to be cheap. All the computing resources that are responsible for delivering SaaS are totally managed by the vendor. The service is accessible through a web browser or lightweight client applications.
End customers use SaaS regularly. The most popular SaaS providers offer the following products and services:
Google Ecosystem including Gmail, Google Docs, Google Drive, Microsoft Office 365 and SalesForce.
PaaS - Platform as a Service
This service is mostly a development environment that is made up of a programming language execution environment, an operating system, web server, and database. It provides an environment where users can build, compile, and run their program without worrying about an hidden infrastructure. You manage the data and application resources. All the other resources are managed by the vendor. This is the realm for developers. PaaS providers offer e.g. the following products and services:
Amazon Web services, Google App Engine, Windows Azure and Heroku
IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service
This service provides the architecture and infrastructure. It provides all computing resources but in a virtual environment so multiple users can have access. The resources include data storage, virtualization, servers, and networking. Most vendors are responsible for managing them. If you use this service, you are responsible for handling other resources including applications, data, runtime, and middleware. This is mostly for SysAdmins. IaaS providers offer the following products and services:
Amazon EC2, Go Grid and Rackspace.com.
For more information, watch this video clip: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wB6Lfdo2m1Q&pbjreload=101
Source: IBM Cloud Learn Hub https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCKWaEZ-_VweaEx1j62do_vQ?pbjreload=101
References:
- http://faculty.winthrop.edu/domanm/csci411/Handouts/NIST.pdf
- Img src: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mahmoud_Maqableh/publication/284163241/figure/fig1/AS:297257250377728@1447883059328/Figure-1-Cloud-computing-service-models-deployment-models-and-essential-and-common.png
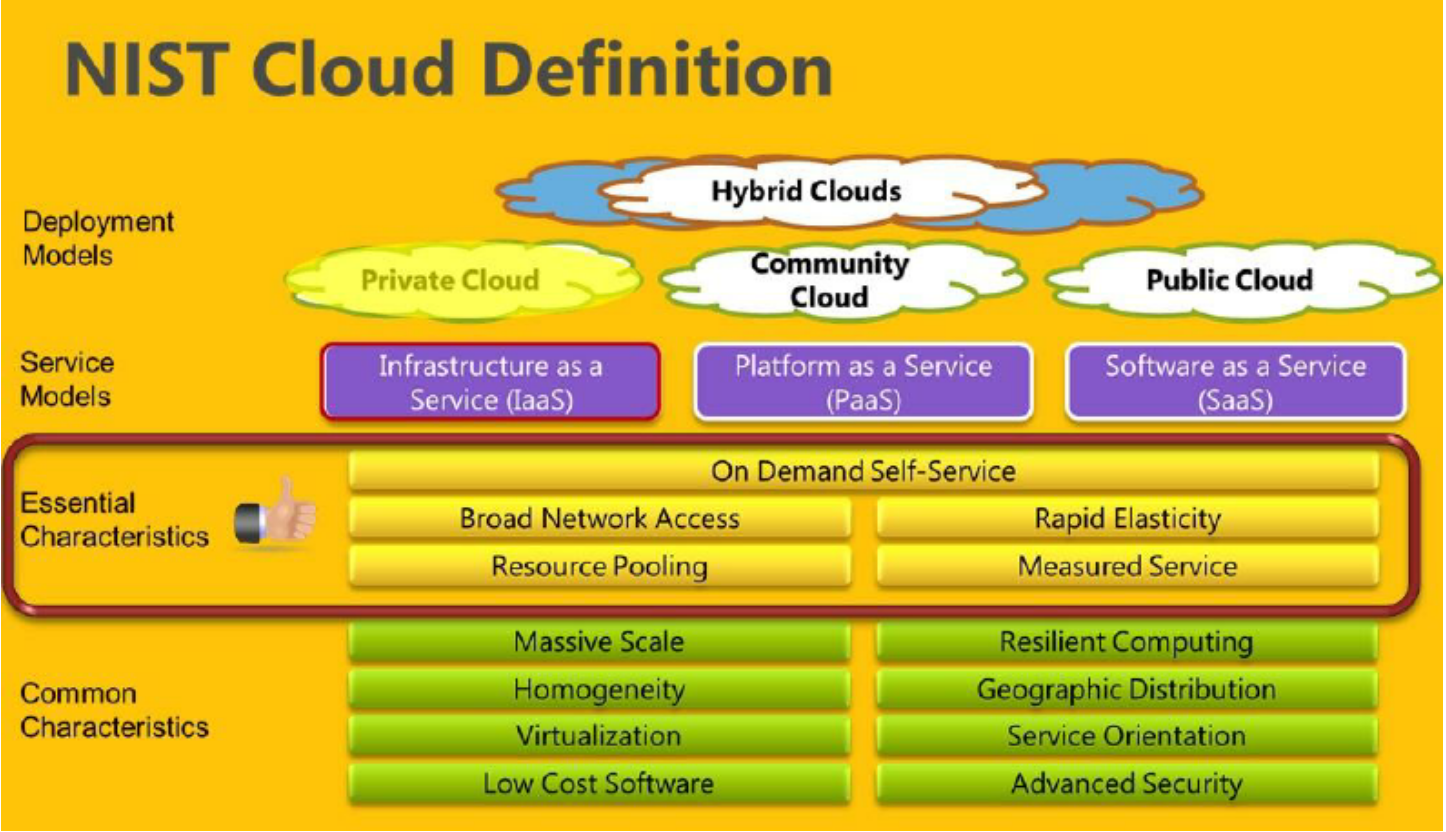
Picture 2. Cloud Model.
Model for Cloud Computing Deployment
The cloud deployment model specifies the type of cloud environment which is primarily distinguished by the ownership, access and size. The deployment model influences the reliability, scalability, security and cost. There are 4 primary cloud deployment models as we can see Picture 3. Cloud deployment models are:
- Private Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud

Picture 3. Cloud Deployment Model. Img src: http://www.thecloudway.net/images/deployment-models.jpg
Private Cloud
The private cloud deployment model emulates public cloud service offerings within an organisation’s boundaries. The computing infrastructure or services are dedicated to a particular organisation (Not shared with others). It is more expensive and more secure in comparison to the public cloud. Enterprise retains full control over corporate data, security guidelines, and system performance. The private cloud offerings are usually not as large-scale as public cloud offerings. It is also sometimes referred to as internal cloud and is implemented in a secure environment that is under the governance of the IT department belonging to a particular corporate. The figure on the right shows a cloud service consumer that host infrastructure in the organisation's on-premise environment.
Public Cloud
Public Cloud is a deployment model in which service/services are provided over a network that is open for public use. Public cloud services may be free or the cost of use is based on the pay-per-usage model. Cloud services and cloud resources are procured from very large resource pools that are shared by all end users and various organisations. The public cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft and Google own and operate the infrastructure at their data centre and access are generally via the Internet. The Picture 4 below shows a partial view of the public cloud deployment model.
Community Cloud
Community Cloud deployment model is a generalisation of private cloud. Organisations with similar requirements, security concerns, compliances and jurisdiction share a cloud infrastructure. The cloud infrastructure is hosted internally or externally which is managed internally or by a third party. The costs are spread over involved organisations.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud deployment model is a combination or two or more cloud deployment models. For example, a company can use a private cloud for sensitive data whereas public cloud for less sensitive data. The diagram below shows an organisation adopting both private and public cloud.
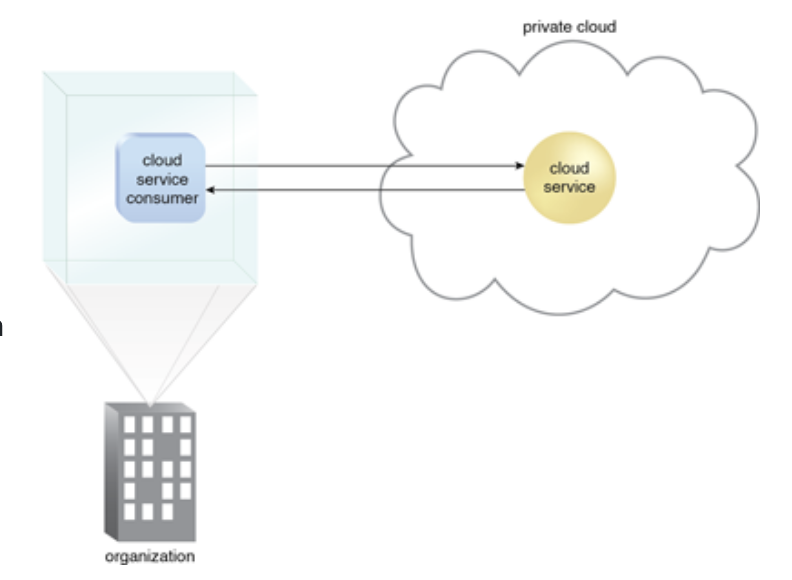
Picture 4. Private cloud. Img Src: http://whatiscloud.com/static/images/chapter4/04fig19.png